Solar Receiver Complex
The RATAN-600 [Brief history and description] radio telescope is one of two main instruments of Special Astrophysical Observatory of Russian Academy of Sciences.


Antenna RATAN-600
Receivers-> Panoramic Analyser of Spectrum
Methods of observations->Periscope System: South Sector+Flat Mirror
Dynamic range of the solar registrations is 30 db. The
maximal accuracy in the measurement of the polarization
degree on the disk is 0.05 % and on the limb is 0.5 %.
Antenna RATAN-600 (from Handbook by Trushkin S.A.)
Antenna of RATAN radio telescope consist of 576-m circle of 895 elements (2 x 11.5 m), which could use as 4 independent sectors (225 elements) of that reflector (named: North, South, West and East). There are tree different feed-cabines (N1,2,3) with secondary mirrors. With central rail-way rotation circle the feed-cabines could move in any of 12 fixed azimiths.
The RATAN-600 can be used for observations in four different modes; these modes are illustrated by the diagram.
(1) It is possible to simultaneously carry out independent observing programs using individual sectors at various discrete azimuths and secondary mirrors on corresponding railway tracks.
Each of these secondary mirrors
is a parabolic cylinder with a horizontal axis, 5.5 m x 8 m in size; the
horizontal angle over which the main mirror is illuminated is 100 – 110o
. The position of the secondary mirror (the focus) on the railway tracks
depends on the elevation above the horizon, which can vary between 0 and
100o and is calculated by a computer at the same time that the coordinates
of the elements included in the sector are calculated. Usually, observations
using a single sector are carried out at a fixed azimuth (i.e., the source
passes through a fixed directivity pattern, with changes from source to
source according to the source elevations (20 – 40 changes per day). In
the process, a one-dimensional image of a source is obtained in each observation.
(2) Two-dimensional images
of sources can be synthesized by combining the one-dimensional images obtained
from a series of successive observations of the same source at different
azimuths.
(3)
The southern sector can operate in combination with the flat periscope
reflector; it then forms a Kraus-type system like those at the University
of Ohio or Nansay, France. It will be possible to track a source by moving
the secondary mirror along the arc-shaped railway tracks after the work
associated with automation is completed.
(4) Finally, using a special
conical secondary mirror installed at the center of the RATAN, it is possible
to collect radiation from the entire ring while observing near the zenith;
the maximum collecting area and resolving power is obtained in this case.
In the end of 1985 a new
conical mirror and feed-cabine N6 was firstly used. That feed-cabine allows
to collect radio emission from whole circle, but range of source declinations
limited in this regime the zone of zenith distance z=±6o (or Dec:
38-49o ).
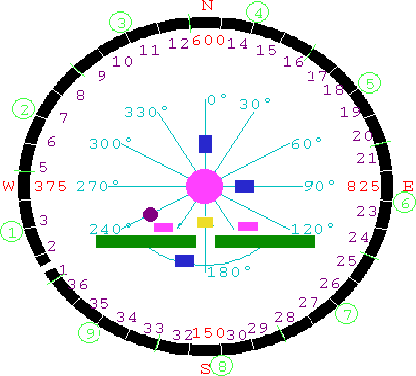 Common
plan of telescope Common
plan of telescope |
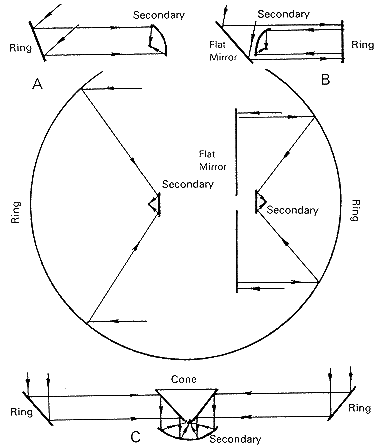
Modes of operation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|